Are you considering a solar generator but wondering how it actually stores the power captured from the sun? It’s a common question, and understanding this is crucial for determining if a solar generator will meet your needs. The good news is that solar generators don’t store power directly as sunlight; they utilize batteries to save energy for later use – much like a portable power station.
This comprehensive guide will break down everything you need to know about how solar generators store power, the types of batteries used, capacity considerations, battery lifespan, and how to maximize your solar generator’s storage potential. By the end of this article, you’ll be confident in understanding how these systems work and whether they’re the right power solution for you.
How Solar Generators Store Power
Solar generators aren’t actually generators in the traditional sense. They don’t burn fuel to create electricity. Instead, they are portable power stations that collect energy from solar panels and store it in rechargeable batteries. The process involves several key components:
- Solar Panels: These capture sunlight and convert it into DC (Direct Current) electricity.
- Charge Controller: This regulates the DC electricity from the solar panels to prevent overcharging the battery. It optimizes the charging process for efficiency and battery health.
- Inverter: This converts the DC electricity stored in the battery into AC (Alternating Current) electricity, which is what most household appliances use.
- Battery: This is the core component where the energy is stored for later use.
Essentially, the solar panels create the power, the charge controller manages it, the inverter makes it usable, and the battery holds it until you need it.
Types of Batteries Used in Solar Generators
The type of battery significantly impacts a solar generator’s performance, lifespan, and cost. Here are the most common types:
Lithium-ion Batteries
- Pros: Lightweight, high energy density (meaning they store a lot of power in a small space), long lifespan (typically 2,000-5,000+ charge cycles), low self-discharge rate.
- Cons: More expensive than other battery types, can be sensitive to extreme temperatures.
- Common Uses: Most modern solar generators utilize lithium-ion batteries due to their superior performance and portability.
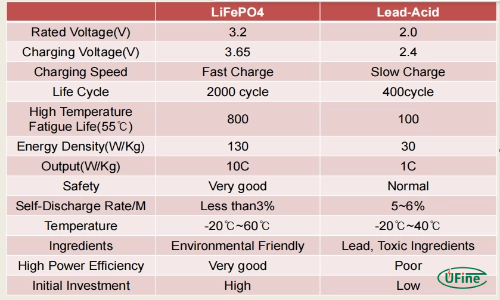
Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) Batteries
- Pros: Extremely safe and stable, very long lifespan (3,000-5,000+ charge cycles), excellent thermal stability, less prone to overheating.
- Cons: Slightly lower energy density than standard lithium-ion, can be more expensive.
- Common Uses: Increasingly popular in higher-end solar generators and applications requiring maximum safety and longevity.
Lead-Acid Batteries (Less Common)
- Pros: Least expensive option.
- Cons: Heavy, low energy density, short lifespan (300-500 charge cycles), require regular maintenance, and have a high self-discharge rate.
- Common Uses: Older or very budget-friendly solar generators. Generally not recommended due to their limitations.
Understanding Solar Generator Capacity (Watt-Hours)

Battery capacity is measured in Watt-hours (Wh). This indicates how much energy the battery can store and for how long.
-
Calculating Run Time: To estimate how long a solar generator can power a device, use this formula:
- Run Time (hours) = Battery Capacity (Wh) / Device Wattage (W)
-
Example: A 500Wh solar generator can power a 50W light bulb for approximately 10 hours (500Wh / 50W = 10 hours).
-
Capacity Needs: Consider your power needs when choosing a solar generator. Smaller generators (200-500Wh) are suitable for charging phones and small devices, while larger generators (1000Wh+) are needed for running appliances like refrigerators or power tools.
Battery Lifespan and Maintenance
The lifespan of a solar generator battery is measured in charge cycles – one complete discharge and recharge.
Factors Affecting Battery Lifespan:
- Depth of Discharge (DoD): Completely discharging a battery shortens its lifespan. Lithium-ion batteries perform best when kept between 20% and 80% charge.
- Temperature: Extreme temperatures (hot or cold) can degrade battery performance and lifespan.
- Charging Habits: Using the correct charger and avoiding overcharging are crucial.
- Storage Conditions: Store the solar generator in a cool, dry place when not in use.
Maintenance Tips:
- Regularly Check Battery Level: Avoid letting the battery completely drain.
- Store Properly: Keep the generator in a temperature-controlled environment.
- Follow Manufacturer’s Instructions: Refer to the user manual for specific maintenance recommendations.
- Partial Charging: For lithium-ion batteries, frequent partial charges are better than infrequent full charges.
Maximizing Your Solar Generator’s Storage Potential

Here are some ways to optimize your solar generator’s storage and performance:
- Choose the Right Battery Type: LiFePO4 batteries offer the longest lifespan and best safety, but lithium-ion is a good balance of performance and cost.
- Properly Size Your System: Match the battery capacity to your energy needs.
- Use Efficient Appliances: LED lights and energy-star rated appliances consume less power.
- Optimize Solar Panel Placement: Ensure your solar panels receive maximum sunlight exposure.
- Monitor Battery Health: Many solar generators have built-in battery management systems that provide information about battery health and usage.
Pro Tips for Solar Generator Power Storage
- Battery Management Systems (BMS): Look for solar generators with a sophisticated BMS. These protect the battery from overcharging, overheating, and deep discharge, extending its lifespan.
- Pass-Through Charging: Some generators allow you to charge the battery while simultaneously powering devices. This is useful for extended outages.
- Expandable Capacity: Some models offer the ability to add extra battery packs to increase storage capacity.
- Cold Weather Considerations: Lithium-ion batteries may have reduced performance in cold temperatures. Consider using a battery warmer or storing the generator indoors.
- Solar Panel Wattage: Pair your solar generator with appropriately sized solar panels for efficient charging.
Professional Help & When to Seek It
- Battery Replacement: If your battery is significantly degraded and no longer holds a charge, professional replacement is often required.
- Inverter Issues: If the inverter is malfunctioning, a qualified technician should diagnose and repair it.
- Complex System Integration: For larger or more complex solar setups, consult with a professional installer.
FAQ
Q: Can I leave a solar generator plugged into the wall if there’s no sun?
A: Yes, most solar generators can be charged from a standard AC outlet. This is useful for topping up the battery or charging it completely when solar power isn’t available.
Q: How long will a fully charged solar generator last?
A: It depends on the battery capacity and the power consumption of the devices you’re using. Refer to the run time calculation described earlier.
Q: Are solar generators safe to use indoors?
A: Yes, as long as they are properly ventilated and used according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Lithium-ion and LiFePO4 batteries are generally very safe, but avoid exposing them to extreme temperatures.
Q: Can I connect multiple solar panels to a solar generator?
A: Yes, but check the specifications of your solar generator to ensure it supports the voltage and wattage of the panels you want to connect.
Enjoy Your Solar Power Solution
By understanding how solar generators store power and following these tips, you can maximize the efficiency and lifespan of your system. You now have the knowledge to choose the right generator for your needs, maintain its performance, and enjoy reliable, off-grid power whenever you need it.
Have you successfully used a solar generator? Share your experience and tips in the comments below to help other readers!