Are you frustrated that your Renogy DC to DC charger isn’t charging your auxiliary battery? It’s a common problem that can leave you stranded or without power when you need it most. A quick fix often involves checking your connections and voltage, but the issue could be more complex.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through troubleshooting your Renogy DC to DC charger, covering everything from the most common causes to advanced solutions. We’ll cover quick fixes, detailed diagnostic steps, and preventative maintenance to ensure your charging system operates reliably. By the end of this article, you’ll have the knowledge and confidence to get your Renogy charger working again and keep your batteries topped up.
Common Causes of Renogy DC to DC Charger Not Charging
Several factors can prevent your Renogy DC to DC charger from functioning correctly. Here’s a breakdown of the most frequent culprits:
Low Input Voltage
The charger requires a sufficient voltage from your vehicle’s alternator to operate. If the input voltage is too low, it won’t initiate charging. This is especially common in older vehicles or those with a weak alternator.
Poor Connections
Loose, corroded, or improperly sized wiring can significantly impede the flow of electricity. This is arguably the most common cause of charging issues.
Blown Fuse
A blown fuse in either the input or output circuit will immediately halt the charging process.
Incorrect Wiring
Reversed polarity or incorrect wiring configurations can damage the charger and prevent it from operating.
Faulty Charger
In some cases, the charger itself may be defective. Internal component failure can occur, requiring replacement.
How to Fix Renogy DC to DC Charger Not Charging

Here are several methods to diagnose and resolve the issue, ranging from simple checks to more involved troubleshooting:
Method 1: Quick Connection and Fuse Check
This is the first and easiest step to rule out common problems.
Diagnosing the Issue
Visually inspect all wiring connections to the charger, battery, and vehicle. Look for loose connections, corrosion, or damaged wires. Check the input and output fuses.
Fix Steps
- Turn off the charger and disconnect both the input and output connections.
- Inspect all wiring: Tighten any loose connections and clean corroded terminals with a wire brush and electrical contact cleaner.
- Check the fuses: Use a multimeter to test the continuity of both input and output fuses. Replace any blown fuses with the same amperage rating. Important: Never use a fuse with a higher amperage rating.
- Reconnect the input and output connections.
- Turn on the charger and observe if charging initiates.
Testing
Start your vehicle and monitor the voltage on the auxiliary battery. If the charger is working, the voltage should increase.
Method 2: Voltage Input Verification
Ensuring adequate input voltage is crucial.
Diagnosing the Issue
Use a multimeter to measure the voltage at the charger’s input terminals while your vehicle is running. The voltage should be within the charger’s specified input range (typically 12V-16V).
Fix Steps
- With the vehicle running, carefully measure the voltage at the charger’s input terminals.
- If the voltage is too low (below 12V), investigate the vehicle’s charging system. This may involve checking the alternator, battery, and wiring.
- If the voltage is within range, proceed to the next troubleshooting step.
Testing
Monitor the input voltage while revving the engine slightly. The voltage should remain stable and within the specified range.
Method 3: Polarity and Wiring Confirmation
Incorrect wiring can cause significant issues.
Diagnosing the Issue
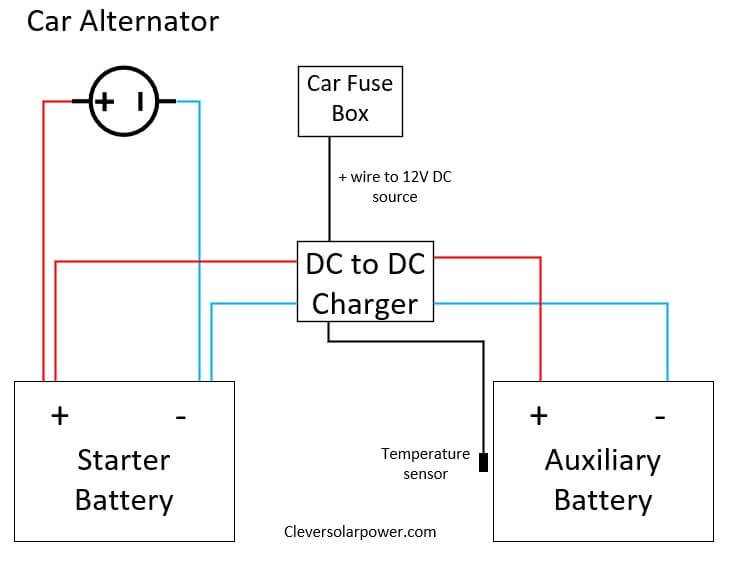
Double-check the polarity of the input and output connections. Positive (+) must connect to positive, and negative (-) to negative. Consult the Renogy charger’s manual for the correct wiring diagram.
Fix Steps
- Disconnect both the input and output connections.
- Carefully verify the polarity of each connection.
- Compare your wiring configuration to the diagram in the Renogy manual.
- Correct any incorrect wiring.
- Reconnect the input and output connections.
Testing
After correcting the wiring, restart your vehicle and monitor the charging process.
Method 4: Charger Reset and Internal Inspection (Advanced)
If the above steps don’t resolve the issue, a reset or internal inspection might be necessary. Warning: This involves opening the charger and should only be attempted if you are comfortable working with electronics.
Diagnosing the Issue
Sometimes, the charger’s internal circuitry can glitch. A reset or visual inspection for damaged components may reveal the problem.
Fix Steps
- Disconnect the charger from all power sources.
- Consult the Renogy manual for instructions on performing a reset (if available).
- If a reset doesn’t work, carefully open the charger’s enclosure. Important: Be extremely cautious when working with electronics. Disconnect the power source and avoid touching any exposed components.
- Visually inspect the internal components for signs of damage, such as burnt resistors or swollen capacitors.
- If you identify any damaged components, consider replacing the entire charger.
Testing
If no visible damage is found and a reset was performed, reconnect the charger and test its functionality.
Preventing Future Charging Issues

Proactive maintenance can prevent many charging problems.
Regular Connection Inspection
Inspect all wiring connections at least monthly for looseness, corrosion, or damage.
Battery Maintenance
Maintain your auxiliary battery according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. This includes regular cleaning, electrolyte level checks (for flooded batteries), and proper storage.
Fuse Replacement
Keep spare fuses of the correct amperage rating on hand for quick replacement.
Proper Wiring Sizing
Ensure that the wiring used for the DC to DC charger is of the appropriate gauge (thickness) to handle the current load. Consult the Renogy manual for recommended wire sizes.
Pro Tips
- Use a Battery Monitor: A battery monitor provides real-time information about voltage, current, and state of charge, helping you identify potential problems early.
- Avoid Deep Discharges: Regularly discharging your auxiliary battery to very low levels can shorten its lifespan and reduce its charging efficiency.
- Protect from Moisture: Keep the charger and wiring protected from moisture and extreme temperatures.
- Check Alternator Output: Periodically have your vehicle’s alternator tested to ensure it’s providing adequate voltage.
- Read the Manual: Always refer to the Renogy DC to DC charger manual for specific instructions and troubleshooting guidance.
Professional Help
If you’ve tried all the troubleshooting steps and your Renogy charger still isn’t working, it’s time to seek professional help.
Signs You Need a Pro
- You’re uncomfortable working with electrical systems.
- You suspect a problem with your vehicle’s charging system.
- You’ve identified damaged internal components within the charger.
Finding a Qualified Technician
Look for a qualified automotive electrician or a specialist in RV/solar power systems.
Typical Cost Ranges
Diagnostic fees typically range from $50-$150. Repair costs can vary depending on the complexity of the problem, but a charger replacement could cost $100-$300+.
FAQ
Q: Why is my Renogy DC to DC charger getting hot?
A: The charger may get warm during operation, especially under heavy load. However, excessive heat could indicate a problem with the internal circuitry. Disconnect the charger and investigate further.
Q: Can I use a Renogy DC to DC charger with any type of battery?
A: Renogy DC to DC chargers are designed for use with various battery types, including AGM, Gel, and Lithium. However, it’s crucial to select the correct charging profile for your specific battery type.
Q: What does the “Boost” and “Bulk” stages mean on my charger?
A: These are charging stages. Bulk is the initial high-current charge, and Boost is a final stage to bring the battery to its full charge voltage.
Q: My charger worked fine before, but now it’s not charging. What could be the issue?
A: This could be due to a loose connection, blown fuse, low input voltage, or a failing component within the charger. Follow the troubleshooting steps outlined in this guide.
Get Your Renogy Charger Working Again
You now have a comprehensive understanding of how to troubleshoot and fix a Renogy DC to DC charger that isn’t charging. Remember to start with the simplest solutions – checking connections and fuses – and work your way towards more advanced troubleshooting steps.
Don’t let a faulty charger ruin your next adventure. By following this guide, you’ll be well-equipped to diagnose and resolve the issue, ensuring your auxiliary battery remains charged and ready to power your off-grid lifestyle.
Have you successfully fixed your Renogy DC to DC charger? Share your experience and any additional tips in the comments below to help other readers!